Transfer-learning-based Autotuning using Gaussian Copula
Quick Links
Media
- arXiv Posting
- Self-Hosted Publication
© Thomas Randall 2023. This is the author’s version of the work. It is posted here for your personal use. Not for redistribution. The definitive version was published in Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Supercomputing (ICS '23), https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3577193.3593712.
- Presentation Slides
- Recorded Presentation
Publication Details
Appears in Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Supercomputing (ICS '23) by authors: Thomas Randall, Jaehoon Koo, Brice Videau, Michael Kruse, Xingfu Wu, Paul Hovland, Mary Hall, Rong Ge, Prasanna Balaprakash
Abstract
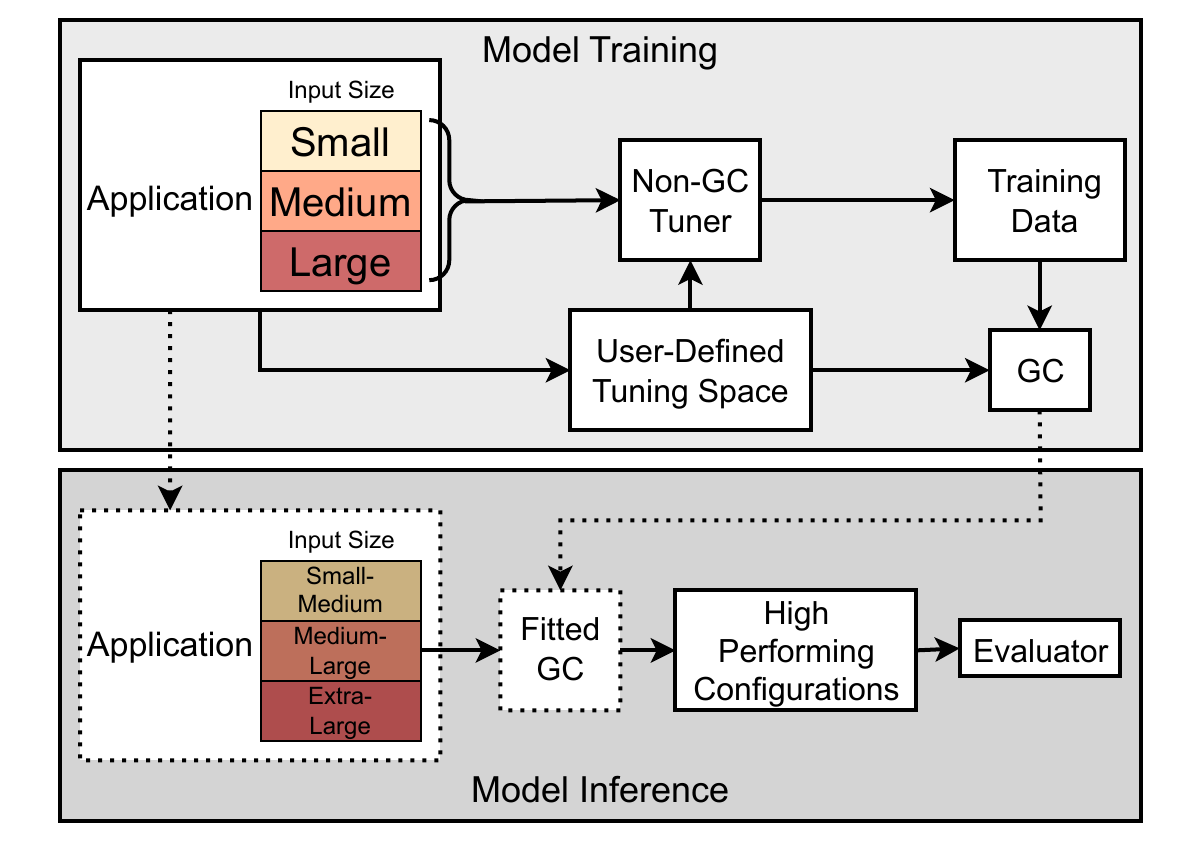
As diverse high-performance computing (HPC) systems are built, many opportunities arise for applications to solve larger problems than ever before. Given the significantly increased complexity of these HPC systems and application tuning, empirical performance tuning, such as autotuning, has emerged as a promising approach in recent years. Despite its effectiveness, autotuning is often a computationally expensive approach. Transfer learning (TL)-based autotuning seeks to address this issue by leveraging the data from prior tuning. Current TL methods for autotuning spend significant time modeling the relationship between parameter configurations and performance, which is ineffective for few-shot (that is, few empirical evaluations) tuning on new tasks. We introduce the first generative TL-based autotuning approach based on the Gaussian copula (GC) to model the high-performing regions of the search space from prior data and then generate high-performing configurations for new tasks. This allows a sampling-based approach that maximizes few-shot performance and provides the first probabilistic estimation of the few-shot budget for effective TL-based autotuning. We compare our generative TL approach with state-of-the-art autotuning techniques on several benchmarks. We find that the GC is capable of achieving 64.37% of peak few-shot performance in its first evaluation. Furthermore, the GC model can determine a few-shot transfer budget that yields up to 33.39× speedup, a dramatic improvement over the 20.58× speedup using prior techniques.